The Role of Genetics in Periodontal Diseases: What You Need to Know?
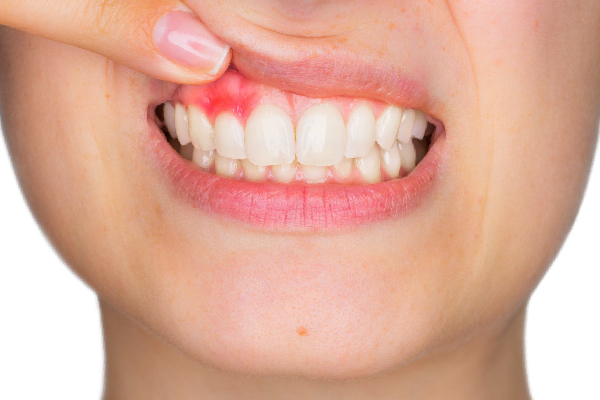
Periodontal diseases, commonly known as gum diseases, affect millions of people worldwide, posing a significant threat to oral health. While factors like poor oral hygiene and smoking are well-established contributors, recent research has shed light on the substantial influence of genetics in the development and progression of these conditions. Understanding the interplay between genetic predisposition and environmental factors is crucial for effective prevention and treatment. In this article, we delve into the various aspects of the role genetics plays in periodontal diseases. Periodontal diseases are broadly classified into two main types: gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis, the milder form, primarily affects the gums, causing inflammation and bleeding. On the other hand, periodontitis is a more severe condition involving the supporting structures of the teeth, such as the bone and ligaments, and can lead to tooth loss if left untreated. Research has shown a hereditary component in the susceptibility to both gingivitis and periodontitis. Genetic factors contribute to variations in the immune response, which can influence an individual's vulnerability to bacterial infections in the gums. Certain gene variations may enhance the inflammatory response, making some individuals more prone to severe gum diseases. Understanding the genetic underpinnings of these conditions can help in identifying individuals at higher risk. Dental professionals, such as those at MaryClinic, are increasingly incorporating genetic screening into their practice to tailor preventive strategies and early intervention for patients with a genetic predisposition to gum diseases. The progression of periodontal diseases is not uniform across individuals. While some may experience a slow and relatively mild deterioration, others may face rapid and severe disease progression. This variation has led researchers to investigate the role of genetics in influencing the course of periodontitis. Several genes have been identified that contribute to the severity and progression of periodontal diseases. For instance, variations in genes related to the regulation of inflammation and immune response can impact the body's ability to control bacterial infection in the gums. Additionally, genetic factors can influence the production and function of collagen, a key component of the connective tissues in the gums. Altered collagen metabolism may compromise the structural integrity of the gums, exacerbating the effects of periodontal diseases. Recognizing the genetic factors involved in disease progression can aid in the development of targeted therapies. Dental professionals, including those at MaryClinic, are at the forefront of adopting personalized treatment approaches that consider an individual's genetic profile to optimize outcomes in managing periodontal diseases. Growing evidence suggests a strong link between periodontal diseases and systemic health conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and rheumatoid arthritis. This intricate connection involves a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors. Certain genetic variations that contribute to an exaggerated inflammatory response may not only exacerbate periodontal diseases but also increase the risk of systemic health issues. Inflammation is a common thread connecting periodontal diseases to conditions like cardiovascular diseases, where chronic inflammation plays a pivotal role. Understanding the genetic links between periodontal diseases and systemic health conditions can pave the way for holistic healthcare approaches. Dental and medical professionals are collaborating more closely, recognizing the importance of addressing both oral and systemic health. Genetic insights enable a comprehensive understanding of an individual's health risks, allowing for more effective preventive measures and coordinated care. As we continue to unravel the genetic mysteries of periodontal diseases, the field of genetic dentistry holds promise for personalized and targeted interventions. Advances in genetic testing technologies and research methodologies are opening new avenues for understanding individual susceptibility and tailoring treatment plans accordingly. The integration of genetic information into routine dental care is becoming increasingly important. Dental clinics, including MaryClinic, are embracing these advancements to provide more effective care. The future of genetic dentistry holds the potential to revolutionize the approach to periodontal health, ushering in an era of personalized medicine where treatment strategies are finely tuned to an individual's genetic makeup. The role of genetics in periodontal diseases is a multifaceted aspect that significantly influences susceptibility, progression, and the interconnectedness with systemic health. Embracing genetic insights in dental care not only enhances our understanding of these conditions but also empowers individuals and healthcare professionals to take proactive measures for optimal oral and overall health.Types of Gum Disease: Deciphering the Genetic Code
Classification of Periodontal Disease: Genes and Disease Progression
Periodontal Disease and Systemic Health: The Genetic Connection
The Future of Genetic Dentistry: Implications for Periodontal Health